When setting up a modern home office, choosing the right materials for your furniture can make a bigger difference than you might think. Two of the most common options, plywood and MDF, both have their strengths and weaknesses, and understanding them can help you create a workspace that is durable, stylish, and functional. Whether you are building a sleek desk, storage units, or shelving, knowing how these materials perform will save you money and frustration in the long run.
Key Takeaways:
- Plywood is stronger and lasts longer, making it ideal for desks and shelves that hold heavy items.
- MDF is best for smooth, painted finishes, perfect for decorative or lightweight furniture.
- Choose based on use and space. Plywood works best for durability and moisture resistance, while MDF suits budget-friendly indoor projects.
In this article, we will break down plywood and MDF, compare their pros and cons, and help you decide which is the best fit for your modern home office setup.
What Is Plywood?
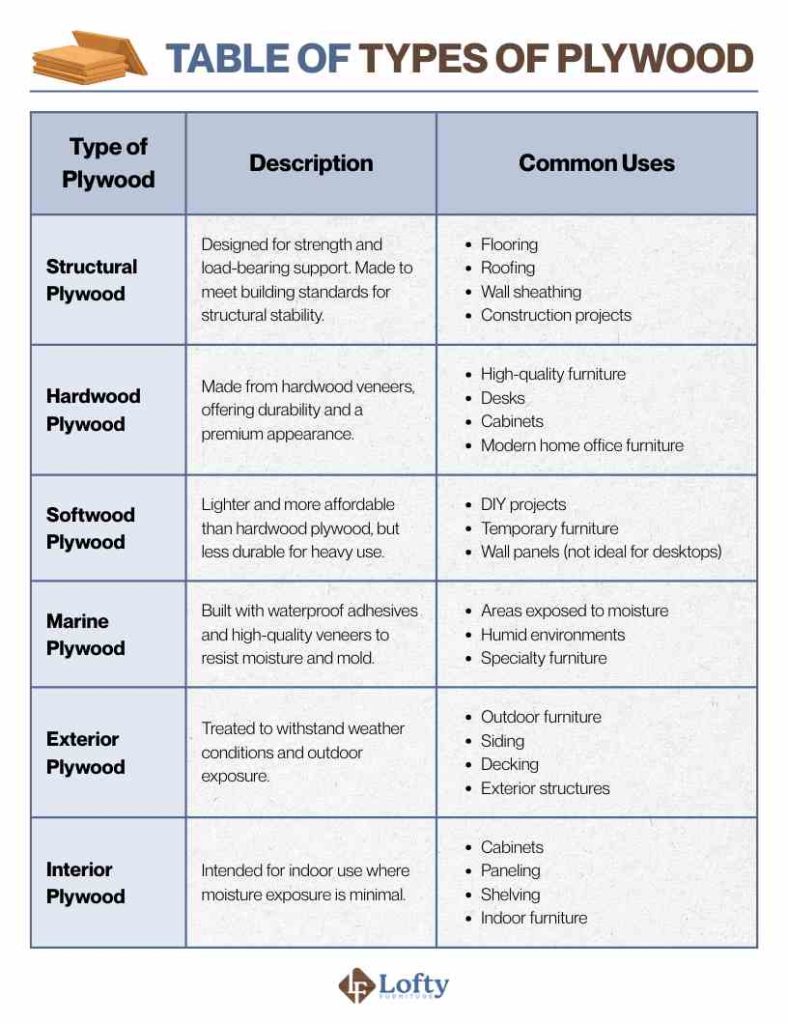
Plywood is a strong, versatile engineered wood made by gluing together thin layers of wood veneer, with each layer’s grain turned at right angles to the next. This cross-grain construction gives plywood its durability, stability, and resistance to cracking or warping compared to solid wood. Because it’s lightweight, affordable, and comes in different grades and thicknesses, plywood is widely used in construction, furniture, cabinetry, and DIY projects where reliable strength and flexibility matter. It comes in different types, each having its own set of advantages and disadvantages depending on the type of project you plan on working on.
What Is MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard)?
MDF, or Medium-Density Fiberboard, is an engineered wood made by compressing fine wood fibers with resin and wax under high heat and pressure, creating a dense, smooth panel with no visible grain. Unlike plywood, it isn’t layered, which gives MDF a uniform surface that’s perfect for painted finishes and clean, modern designs, especially popular in home office furniture. This cheap wood is heavier than plywood but easier to cut and shape without splintering, making it ideal for detailed work like desks, cabinets, shelves, and decorative panels.
Its growing popularity is backed by research too: according to Grand View Research, the global MDF market was valued at USD 44.15 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 82.24 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.2%, driven by rising demand in construction, furniture, and interior design—proof of MDF’s versatility and cost-effectiveness as a strong alternative to plywood.

Plywood vs MDF: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Choosing the right material for your home office furniture can impact everything from durability and cost to appearance and longevity. Understanding the key differences between plywood and MDF helps you make informed decisions that balance function, style, and budget.
Strength and Durability
Plywood is valued for its strength and long-term durability, making it ideal for modern home office furniture used daily. Its layered construction helps evenly distribute weight, allowing desks and shelves to support heavy items without sagging. In a study plywood furniture was found to typically last 15 to 25+ years when properly maintained.
MDF is better suited for lighter-duty furniture and decorative applications. While dense and smooth, it is more prone to sagging under continuous weight. This performance difference is further explained in a detailed MDF durability analysis, which notes that MDF furniture generally lasts around 10 to 20 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions.
Resistance to Moisture and Warping
Plywood handles moisture and humidity better thanks to its cross-grain layers, which reduce warping and swelling. When properly sealed, it can tolerate small spills or changes in humidity, making it a safer option for home offices near windows or in areas with fluctuating moisture levels.
MDF is much more sensitive to moisture and can swell, soften, or deteriorate if exposed to water or high humidity. Because of this, it’s best used strictly in dry, climate-controlled indoor spaces where moisture exposure is unlikely.
Workability and Finishing

Plywood is sturdy once assembled, but it can splinter during cutting if not handled carefully. It works especially well with stains, veneers, or clear finishes that highlight its natural wood grain, making it a good choice for classic or natural-looking office furniture.
MDF is very easy to cut, shape, and machine, which makes it ideal for detailed designs, curved edges, and custom pieces. Its smooth, uniform surface accepts paint evenly, resulting in a clean, modern finish that’s popular in contemporary home offices.
Cost Comparison
Plywood generally costs more upfront than MDF. But it often delivers better long-term value due to its strength and durability in high-use furniture. Typical retail prices for a 4 × 8 ft plywood sheet in the U.S. range roughly from $45 to $90+ per sheet for common furniture-grade panels, with some hardwood plywood options costing more depending on species and grade.
MDF is typically more affordable. Standard 4 × 8 ft MDF panels at major U.S. home centers often cost around $45 to $50 per sheet for ½ in to ¾ in thickness. This is cheaper than similar plywood options.
Environmental Considerations
Plywood can be an environmentally responsible option when sourced from sustainably managed forests. It typically contains lower levels of formaldehyde compared to some engineered woods. This makes it a healthier choice for indoor air quality.
MDF is made from recycled wood fibers, which helps reduce waste, but it often uses formaldehyde-based resins. Low-formaldehyde and eco-certified MDF options are available and should be chosen to improve indoor air safety.
Best Uses in a Modern Home Office

Plywood is best for furniture that requires strength and durability. This includes desks, heavy-duty shelving, and cabinets designed to hold substantial weight. It’s also a great option if you want a natural raw wood look or veneered finish.
According to Mike Bowman, the Technical Product Manager and Lead Editor of Patio Productions:
“For most home office setups, I would recommend the use of 0.75-inch cabinet grade plywood due to its 14.9% lower weight than MDF as well as providing twice the shelf-span strength. In my experience, DIY builders often select MDF in order to obtain a smooth paintable finish but the same finish can be achieved by applying a high build primer to the plywood.”
MDF works best for furniture with smooth, painted surfaces and detailed designs. This includes decorative cabinets, lightweight shelving, and storage units that won’t carry heavy loads. It’s ideal when style and finish matter more than structural strength.
Conclusion
Both plywood and MDF have unique strengths. The best wood choice depends on your specific needs and the type of furniture you’re planning. Plywood is ideal for durability, strength, and moisture resistance. It’s perfect for desks, heavy shelves, and cabinets that will see daily use. It also works well for natural wood finishes or veneered surfaces.
MDF, on the other hand, is great for detailed designs, smooth painted finishes, and projects on a tighter budget. It works best for lightweight shelving, decorative storage, or furniture where aesthetics matter more than heavy load-bearing capacity. Ultimately, your decision should be guided by your project’s function, design, and long-term goals to create a modern home office that meets both style and practicality.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is plywood or MDF better for soundproofing?
Plywood is better for soundproofing in a home office because its layered structure is denser and more solid. MDF can also block sound, but thinner MDF panels may vibrate more. This makes plywood the stronger choice for reducing noise from floors or walls.
Which material is more flexible for curved designs?
MDF is more suitable for curved or detailed designs in furniture and shelving. Its smooth, uniform surface allows easy cutting, shaping, and molding without splintering. This makes it perfect for custom desks, cabinets, or decorative panels.
Which material performs better in high-heat environments?
Plywood handles heat better than MDF. MDF can warp, swell, or release resins when exposed to high temperatures. Plywood is safer for desks placed near heaters, electronics, or areas with lots of sunlight.
